NASA’s Webb Detects Thick Atmosphere Around Broiling Lava World
Researchers using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope have detected the strongest evidence yet for an atmosphere on a rocky

Researchers using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope have detected the strongest evidence yet for an atmosphere on a rocky planet outside our solar system, as NASA leads the world in exploring the universe from the Moon to Mars and beyond. Observations of the ultra-hot super-Earth TOI-561 b suggest that the exoplanet is surrounded by a thick blanket of gases above a global magma ocean. The results help explain the planet’s unusually low density and challenge the prevailing wisdom that relatively small planets so close to their stars are not able to sustain atmospheres.
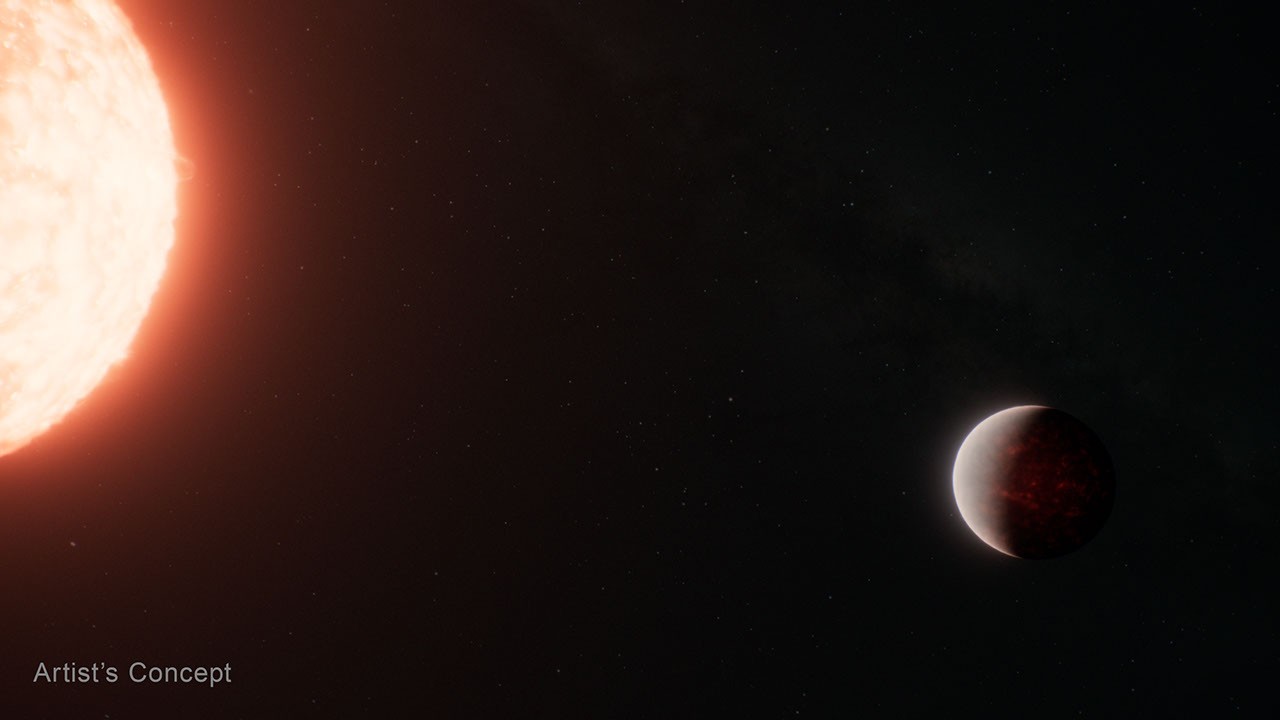
This artist’s concept shows what the hot super-Earth exoplanet TOI-561 b and its star could look like based on observations from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope and other observatories. Webb data suggests that the planet is surrounded by a thick atmosphere above a magma ocean.
Illustration: NASA, ESA, CSA, Ralf Crawford (STScI)
With a radius roughly 1.4 times Earth’s, and an orbital period less than 11 hours, TOI-561 b falls into a rare class of objects known as ultra-short period exoplanets. Although its host star is only slightly smaller and cooler than the Sun, TOI-561 b orbits so close to the star — less than one million miles (one-fortieth the distance between Mercury and the Sun) — that it must be tidally locked, with the temperature of its permanent dayside far exceeding the melting temperature of typical rock.
“What really sets this planet apart is its anomalously low density,” said Johanna Teske, staff scientist at Carnegie Science Earth and Planets Laboratory and lead author on a paper published Thursday in The Astrophysical Journal Letters. “It’s not a super-puff, but it is less dense than you would expect if it had an Earth-like composition.”

An artist’s concept shows what a thick atmosphere above a vast magma ocean on exoplanet TOI-561 b could look like. Measurements captured by NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope suggest that in spite of the intense radiation it receives from its star, TOI-561 b is not a bare rock.
Illustration: NASA, ESA, CSA, Ralf Crawford (STScI)
One explanation the team considered for the planet’s low density was that it could have a relatively small iron core and a mantle made of rock that is not as dense as rock within Earth. Teske notes that this could make sense: “TOI-561 b is distinct among ultra-short period planets in that it orbits a very old (twice as old as the Sun), iron-poor star in a region of the Milky Way known as the thick disk. It must have formed in a very different chemical environment from the planets in our own solar system.” The planet’s composition could be representative of planets that formed when the universe was relatively young.
But an exotic composition can’t explain everything. The team also suspected that TOI-561 b might be surrounded by a thick atmosphere that makes it look larger than it actually is. Although small planets that have spent billions of years baking in blazing stellar radiation are not expected to have atmospheres, some show signs that they are not just bare rock or lava.
To test the hypothesis that TOI-561 b has an atmosphere, the team used Webb’s NIRSpec (Near-Infrared Spectrograph) to measure the planet’s dayside temperature based on its near-infrared brightness. The technique, which involves measuring the decrease in brightness of the star-planet system as the planet moves behind the star, is similar to that used to search for atmospheres in the TRAPPIST-1 system and on other rocky worlds.
If TOI-561 b is a bare rock with no atmosphere to carry heat around to the nightside, its dayside temperature should be approaching 4,900 degrees Fahrenheit (2,700 degrees Celsius). But the NIRSpec observations show that the planet’s dayside appears to be closer to 3,200 degrees Fahrenheit (1,800 degrees Celsius) — still extremely hot, but far cooler than expected.
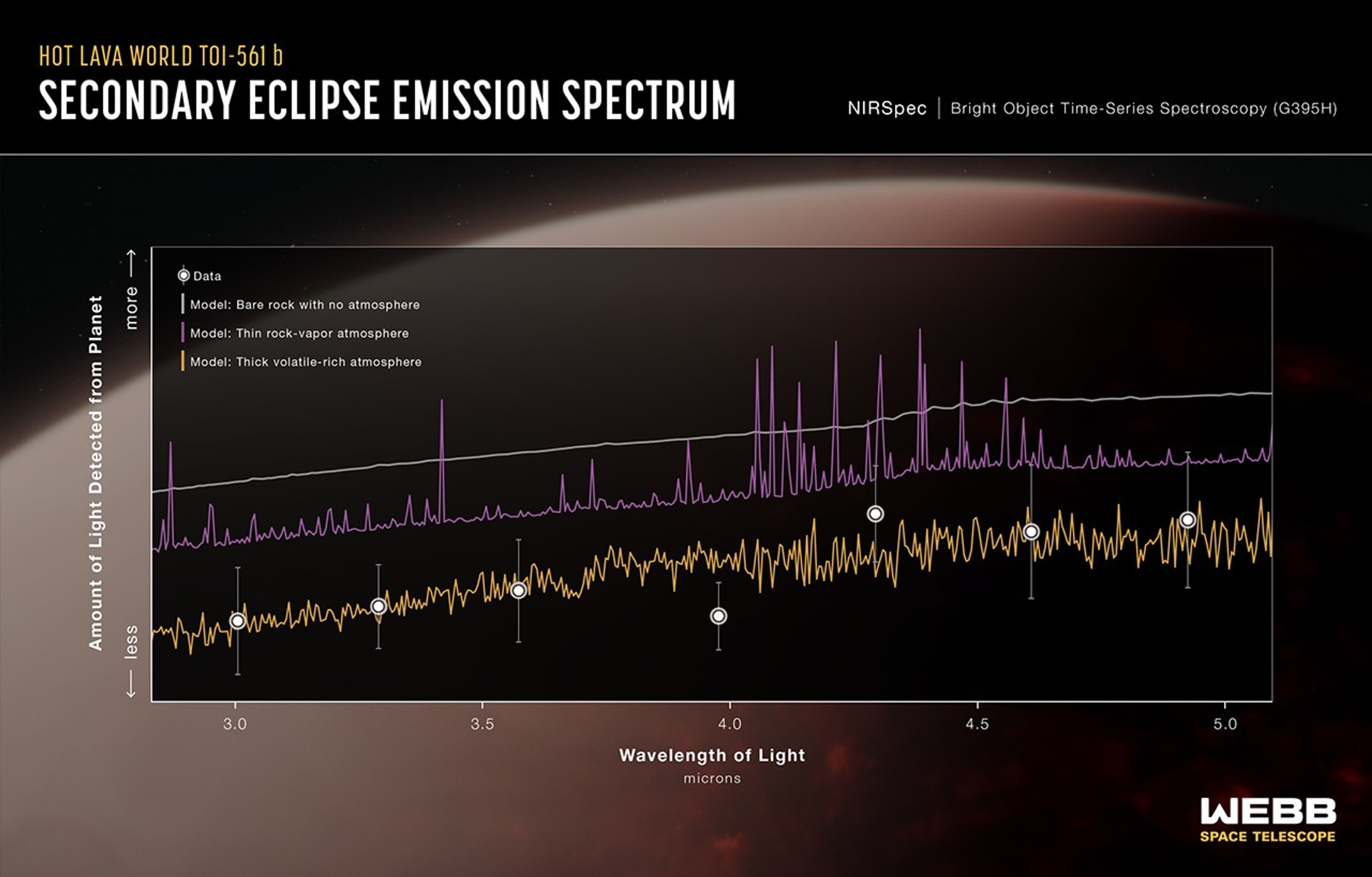
Illustration: NASA, ESA, CSA, Ralf Crawford (STScI); Science: Johanna Teske (Carnegie Science Earth and Planets Laboratory), Anjali Piette (University of Birmingham), Tim Lichtenberg (Groningen), Nicole Wallack (Carnegie Science Earth and Planets Laboratory)
To explain the results, the team considered a few different scenarios. The magma ocean could circulate some heat, but without an atmosphere, the nightside would probably be solid, limiting flow away from the dayside. A thin layer of rock vapor on the surface of the magma ocean is also possible, but on its own would likely have a much smaller cooling effect than observed.
“We really need a thick volatile-rich atmosphere to explain all the observations,” said Anjali Piette, coauthor from the University of Birmingham, United Kingdom.
“Strong winds would cool the dayside by transporting heat over to the nightside. Gases like water vapor would absorb some wavelengths of near-infrared light emitted by the surface before they make it all the way up through the atmosphere. (The planet would look colder because the telescope detects less light.) It’s also possible that there are bright silicate clouds that cool the atmosphere by reflecting starlight.”
While the Webb observations provide compelling evidence for such an atmosphere, the question remains: How can a small planet exposed to such intense radiation can hold on to any atmosphere at all, let alone one so substantial? Some gases must be escaping to space, but perhaps not as efficiently as expected.
“We think there is an equilibrium between the magma ocean and the atmosphere. At the same time that gases are coming out of the planet to feed the atmosphere, the magma ocean is sucking them back into the interior,” said co-author Tim Lichtenberg from the University of Groningen in the Netherlands. “This planet must be much, much more volatile-rich than Earth to explain the observations. It’s really like a wet lava ball.”
These are the first results from Webb’s General Observers Program 3860, which involved observing the system continuously for more than 37 hours while TOI-561 b completed nearly four full orbits of the star. The team is currently analyzing the full data set to map the temperature all the way around the planet and narrow down the composition of the atmosphere.
“What’s really exciting is that this new data set is opening up even more questions than it’s answering,” said Teske.
The James Webb Space Telescope is the world’s premier space science observatory. Webb is solving mysteries in our solar system, looking beyond to distant worlds around other stars, and probing the mysterious structures and origins of our universe and our place in it. Webb is an international program led by NASA with its partners, ESA (European Space Agency) and CSA (Canadian Space Agency).
To learn more about Webb, visit:
Read more: Can Rocky Worlds Orbiting Red Dwarf Stars Maintain Atmospheres?
Explore more: ViewSpace Exoplanet Variety: Atmosphere
Explore more: How to Study Exoplanets: Webb and Challenges
Explore more: How Do We Learn About a Planet’s Atmosphere?
Read more: NASA’s Webb Hints at Possible Atmosphere Surrounding Rocky Exoplanet







