CISA Adds Actively Exploited XSS Bug CVE-2021-26829 in OpenPLC ScadaBR to KEV
The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has updated its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog to include a

The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has updated its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog to include a security flaw impacting OpenPLC ScadaBR, citing evidence of active exploitation.
The vulnerability in question is CVE-2021-26829 (CVSS score: 5.4), a cross-site scripting (XSS) flaw that affects Windows and Linux versions of the software via system_settings.shtm. It impacts the following versions –
- OpenPLC ScadaBR through 1.12.4 on Windows
- OpenPLC ScadaBR through 0.9.1 on Linux
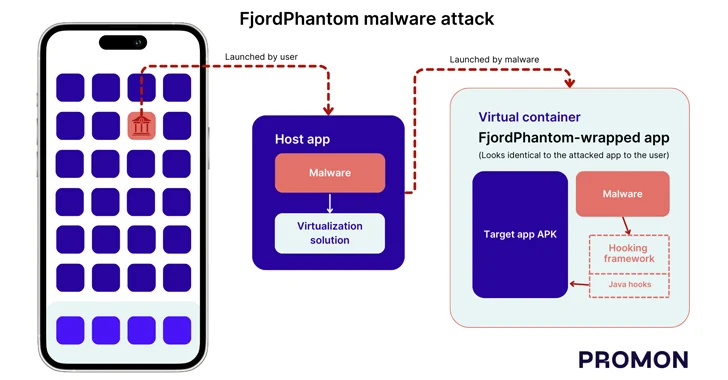
The addition of the security defect to the KEV catalog comes a little over a month after Forescout said it caught a pro-Russian hacktivist group known as TwoNet targeting its honeypot in September 2025, mistaking it for a water treatment facility.
In the compromise aimed at the decoy plant, the threat actor is said to have moved from initial access to disruptive action in about 26 hours, using default credentials to obtain a foothold, followed by carrying out reconnaissance and persistence activities by creating a new user account named “BARLATI.”
The attackers then proceeded to exploit CVE-2021-26829 to deface the HMI login page description to display a pop-up message “Hacked by Barlati,” and modify system settings to disable logs and alarms unaware that they were breaching a honeypot system.
 |
| TwoNet Attack Chain |
“The attacker did not attempt privilege escalation or exploitation of the underlying host, focusing exclusively on the web application layer of the HMI,” Forescout said.
TwoNet began its operations on Telegram earlier this January, initially focusing on distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, before pivoting to a broader set of activities, including the targeting of industrial systems, doxxing, and commercial offerings like ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS), hack-for-hire, and initial access brokerage.
It has also claimed to be affiliated with other hacktivist brands such as CyberTroops and OverFlame. “TwoNet now mixes legacy web tactics with attention-grabbing claims around industrial systems,” the cybersecurity company added.
In light of active exploitation, Federal Civilian Executive Branch (FCEB) agencies are required to apply the necessary fixes by December 19, 2025, for optimal protection.
OAST Service Fuels Exploit Operation
The development comes as VulnCheck said it observed a “long-running” Out-of-Band Application Security Testing (OAST) endpoint on Google Cloud driving a regionally-focused exploit operation. Data from internet sensors deployed by the firm shows that the activity is aimed at Brazil.
“We observed roughly 1,400 exploit attempts spanning more than 200 CVEs linked to this infrastructure,” Jacob Baines, VulnCheck CTO, said. “While most of the activity resembled standard Nuclei templates, the attacker’s hosting choices, payloads, and regional targeting did not align with typical OAST use.”
The activity entails exploiting a flaw and recording successful attempts by issuing an HTTP request to one of the attacker’s OAST subdomains (“*.i-sh.detectors-testing[.]com”). The OAST callbacks associated with the domain date back to at least November 2024, suggesting it has been ongoing for about a year.
The attempts have been found to emanate from U.S.-based Google Cloud infrastructure, illustrating how bad actors are weaponizing legitimate internet services to evade detection and blend in with normal network traffic.
VulnCheck said it also identified a Java class file (“TouchFile.class”) hosted on the IP address (“34.136.22[.]26”) linked to the OAST domain that expands on a publicly available exploit for a Fastjson remote code execution flaw to accept commands and URL parameters, and execute those commands and make outbound HTTP requests to the URLs passed as input.
“The long-lived OAST infrastructure and the consistent regional focus suggest an actor that is running a sustained scanning effort rather than short-lived opportunistic probes,” Baines said. “Attackers continue to take off-the-shelf tooling like Nuclei and spray exploits across the internet to quickly identify and compromise vulnerable assets.”
Update
On December 3, 2025, CISA also added another vulnerability in OpenPLC ScadaBR (CVE-2021-26828, CVSS score: 8.8) to its KEV catalog, requiring FCEB agencies to apply mitigations per vendor instructions by December 24, 2025.
“OpenPLC ScadaBR contains an unrestricted upload of a file with a dangerous type vulnerability that allows remote authenticated users to upload and execute arbitrary JSP files via view_edit.shtm,” the agency said.
It’s worth noting that the exploitation of CVE-2021-26828 was also highlighted by Forescout in the same report published in October 2025, stating it detected “unclaimed activity” on its honeypots between March 1 and 3, 2025, from two Russia-linked IP addresses.
One of the IP addresses, 45.14.247[.]87, “logged into the HMI with default credentials, then exploited CVE-2021-26828 (arbitrary file inclusion in view_edit.shtm) to upload a Java-based web shell,” the company said. “Post-upload actions were limited to basic host enumeration (listing files/processes). No HMI browsing or additional steps observed.”
(The story was updated after publication on December 4, 2025, to include CISA’s addition of CVE-2021-26828 to the KEV catalog.)