The West Faces Snow Drought
The mountains of the western United States are sporting thin winter coats in early 2026. Although most regions saw
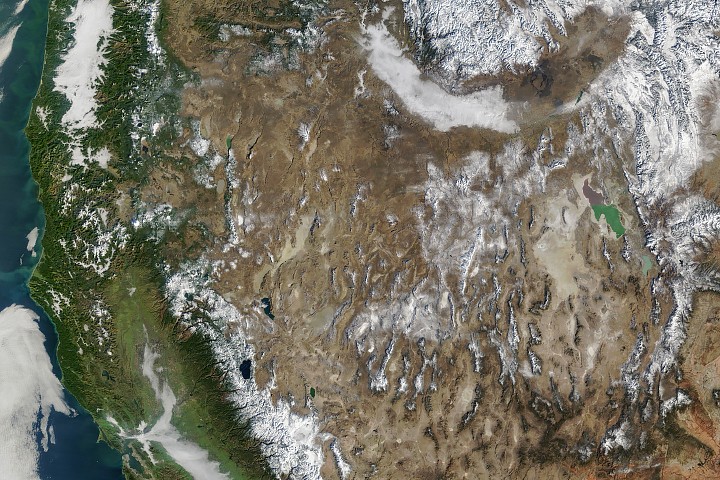
The mountains of the western United States are sporting thin winter coats in early 2026. Although most regions saw average or above-average precipitation in fall and early winter, warmer temperatures meant that much of it fell as rain. The result has been an unusually low snowpack for this time of year, constituting a snow drought.
This image, acquired with the MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) on NASA’s Terra satellite, provides a wide view of meager western snow cover on January 15. On that day, measurements derived from satellite observations showed that snow blanketed 142,700 square miles (369,700 square kilometers) of the west. That’s the lowest coverage for that date in the MODIS record dating back to 2001 and less than one-third of the median. Coverage had increased slightly by January 26.
In addition to snow cover area, snow water equivalent (SWE)—the amount of water stored in the snowpack—is an important indicator of winter conditions in the West. In early January, the National Integrated Drought Information System reported that snow drought, defined as SWE below the 20th percentile for a given date, was most acute in Washington, Oregon, Colorado, Utah, Arizona, and New Mexico. At least one ground-based monitoring station in every major western watershed recorded the lowest SWE in at least 20 years on January 26, according to data published by the USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service.
Overall, the preceding few months were very wet and warm across the West. For the water year beginning on October 1, 2025, many regions saw average or above-average precipitation. However, record warmth across a vast expanse of the region meant that much of that precipitation fell as rain rather than snow. A December 2025 atmospheric river in the Pacific Northwest was one such warm precipitation event.
One nuance in the snow deficit picture can be found in the Southern Sierra and Northern Rockies, where more precipitation has fallen as snow than rain on the lofty peaks. SWE levels stood above average at some high-elevation locations but were low farther downslope. “This is a classic climate-change, temperature-driven, elevationally dependent snowpack deficit,” said Daniel Swain, climate scientist at the California Institute for Water Resources, in a presentation.
Precipitation falling as rain tends to run off before it can recharge reservoirs and groundwater. On the other hand, winter snowpack that melts in the spring can produce a more metered, sustained water supply. The health of the mountain snowpack has implications for ecosystems, wildfire dynamics, and water availability for agriculture and other uses during drier times of the year.
There is still a lot of winter remaining, and February and March can bring significant amounts of snow. But snowfall in the coming months may not be able to make up for existing deficits. In places such as the Pacific Northwest and the Colorado River Basin that are already dry, snow drought may turn into or exacerbate traditional drought.
NASA Earth Observatory image and chart by Michala Garrison, using MODIS data from NASA EOSDIS LANCE and GIBS/Worldview, and snow cover area data from NSIDC Snow Today. Story by Lindsey Doermann.
- The Conversation (2026, January 8) The western US is in a snow drought, and storms have been making it worse. Accessed January 28, 2026.
- NASA Earthdata Cryosphere. Accessed January 28, 2026.
- National Integrated Drought Information System What Is Snow Drought? Accessed January 28, 2026.
- National Integrated Drought Information System (2026, January 15) Drought Status Update for the Intermountain West. Accessed January 28, 2026.
- National Integrated Drought Information System (2026, January 8) Snow Drought Current Conditions and Impacts in the West. Accessed January 28, 2026.
- National Snow and Ice Data Center (2026) Daily Snow Viewer. Accessed January 28, 2026.
- Rittger, K., et al. (2025) Historical MODIS/Terra L3 Global Daily 500m SIN Grid Snow Cover, Snow Albedo, and Snow Surface Properties. SPIRES_HIST, Version 1. National Snow and Ice Data Center.
- Rittger, K., et al. (2026) Near Real-Time MODIS/Terra L3 Global Daily 500m SIN Grid Snow Cover, Snow Albedo, and Snow Surface Properties. SPIRES_NRT, Version 1. National Snow and Ice Data Center.
- USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service (2026) Snow and Water Interactive Map. Accessed January 28, 2026.
- Weather West (2026, January 19) “Warm West/Cool East” dipole to develop over North America in late January; mostly dry/warm conditions lead to record-low Western U.S. snowpack. Accessed January 28, 2026.