Stop treating your pet like a fur baby – you’re damaging its health
Where once they lived in our backyards, many pets – for better and for worse – have now transitioned
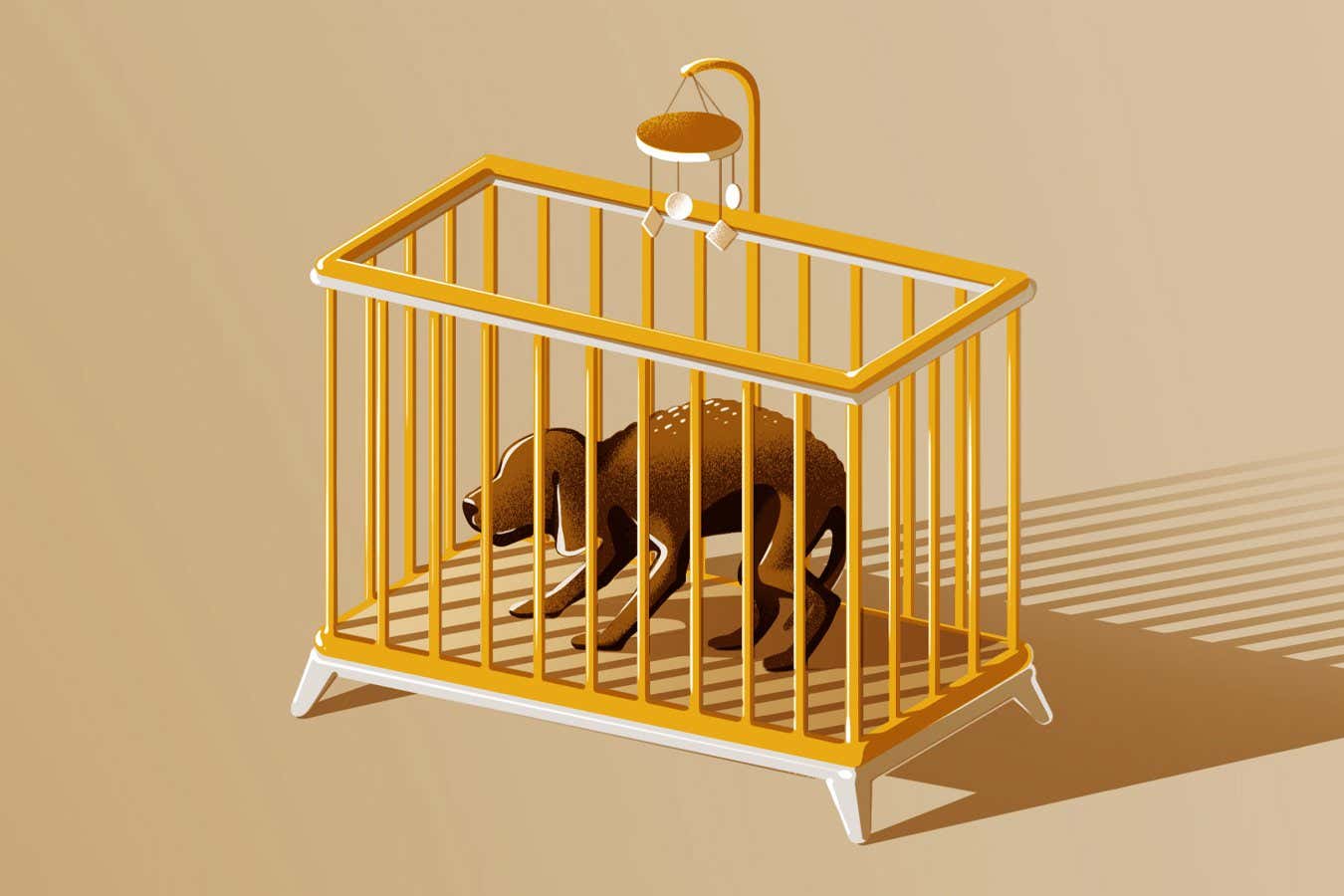

Where once they lived in our backyards, many pets – for better and for worse – have now transitioned to a pampered life as “fur baby” family members. The American Veterinary Medical Association recently highlighted that pet owners were projected to spend nearly $1 billion on costumes for their pets this year. Many see this as harmless fun, but the increasing tendency to treat pets as surrogate children – or at least small humans – can have severe health and welfare consequences for the animals involved.
The forerunners of the modern fur baby belonged to a widely distributed population of small, domesticated carnivores of the genera Canis and Felis. Despite being relatively short-lived, such pets usually brought considerable pleasure, companionship and some health benefits to their human owners, while teaching children a respect for, and the vital requirements of, these animals.
Pets have also brought other educational gains, such as the opportunity to experience and grieve non-human death in preparation for the demise of human loved ones. Most pets would be rewarded for this with food, water, shelter, vaccines, flea powders and a name reflecting their service (Fido), colour (Sooty) or behavioural traits (Rover). Importantly, they were usually assured a relatively pleasant death before the inevitable effects of advanced age extinguished any remaining quality of life.
The pet-to-fur-baby evolution can be attributed to many things, including undue emphasis on the human-animal bond, increasing affluence, ignorance of animals’ biological needs, irresistible consumerism – and, in propagating ill-advised (though well-intentioned) anthropomorphism, social media. The principal causes, drivers and outcomes of fur babyism have intensified and spread globally. Evidence for this is inescapable and goes beyond the availability of clothes for birthdays, Halloween or Christmas. Strollers, jewellery, fragrances, nappies, nail polish, coat dyes, birthday cakes and shoes are now available for the modern fur baby, as are “gold standard” veterinary treatments.
The adverse physical and psychological health effects of fur babyism are well documented. Take strollers for dogs: while potentially useful for injured or arthritic animals, their excessive use in other dogs can lead to muscle wastage, joint damage and obesity. Restricting the fur baby’s movement limits its natural inclination to explore, mark territory and interact with environmental features, such as others of its species, leading to fear and anxiety.
Given these potential health and welfare hazards, one would expect the veterinary profession to adopt a universally condemnatory position with respect to the fur baby phenomenon. Oddly, this isn’t the case, with attitudes ranging from censure to capitalisation. The latter position is troubling because in encouraging overtreatment, for example radiotherapy in geriatric animals, it may further compromise animal welfare without necessarily improving animal health.
An owner’s profound love for their pet can always be accepted, provided the animal’s interests are prioritised, which includes ensuring them freedom from pain, suffering and distress. What is considerably less defensible is the vet who cashes in on an owner’s misguided love for their pet to conduct unnecessary, invasive, painful, unproven and expensive tests and procedures on an animal that cannot give its consent.
All caregivers should reflect on the suffering that may arise when animals are treated inappropriately: that is, as children rather than dogs or cats. And vets pandering to the fur baby trend should know better.
Eddie Clutton is co-author of Veterinary Controversies and Ethical Dilemmas (Routledge)
Topics: